By becoming a member of our site, you can add the content you like to your favorites, and present the content you have produced or liked on the internet to our site visitors with the send content option.
Zaten bir üyeliğiniz mevcut mu ? Giriş yapın
By becoming a member of our site, you can add the content you like to your favorites, and present the content you have produced or liked on the internet to our site visitors with the send content option.
You Can Benefit from All Options Exclusive to Our Members by Registering

Next Content:
Biotechnology in Space: Farming on Mars
- Home Page
- #Healthcare
- Stem Cells in Regenerative Medicine
Stem Cells in Regenerative Medicine
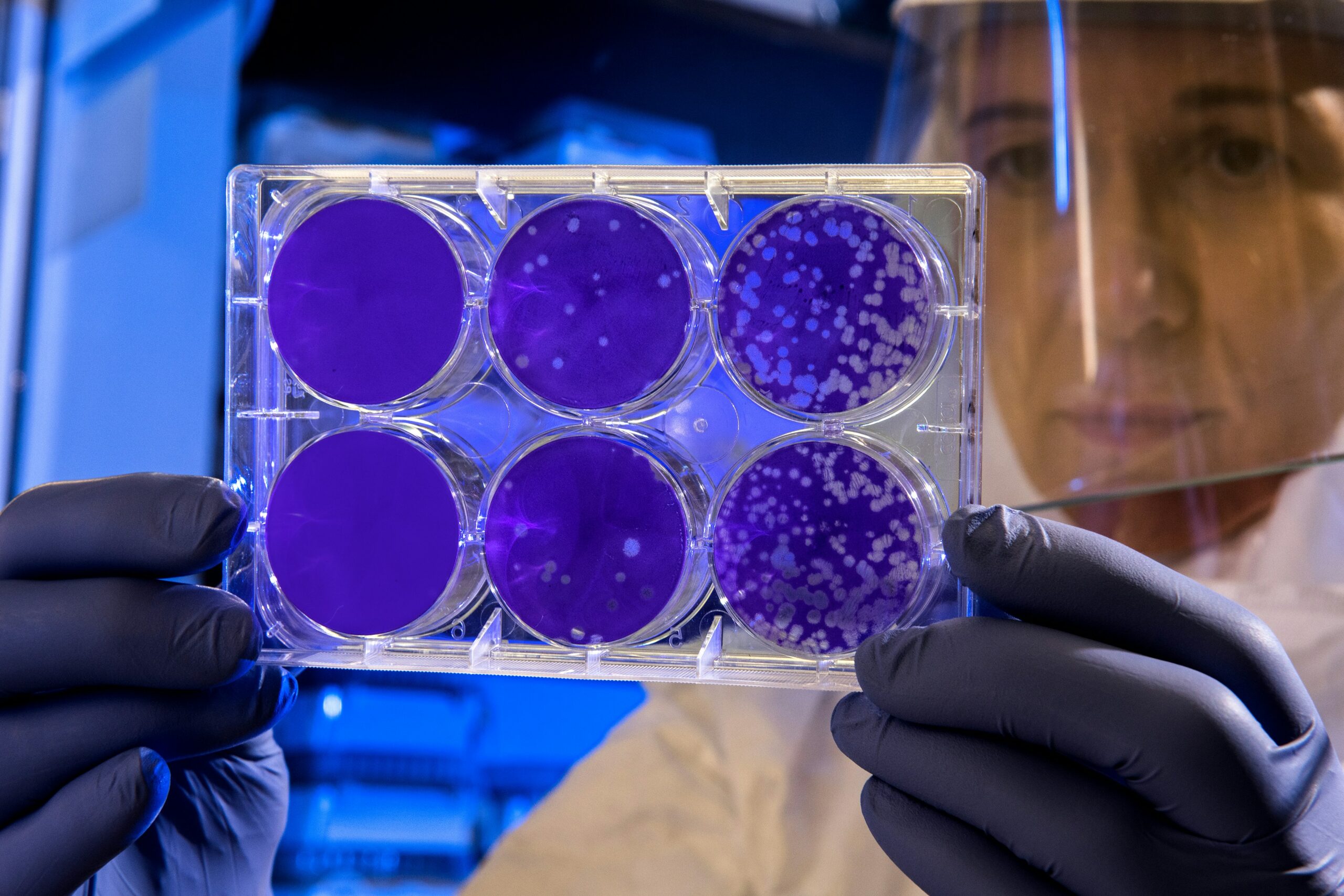
Regenerative medicine is making remarkable strides with the advent of stem cell therapy, offering new hope for treating a range of previously untreatable conditions. This groundbreaking field leverages the unique capabilities of stem cells to repair and regenerate damaged tissues and organs, transforming the landscape of modern medicine.
One of the most significant advances in regenerative medicine is the development of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs). These cells are created by reprogramming adult cells to a pluripotent state, allowing them to differentiate into any cell type in the body. This innovation has opened up new possibilities for personalized medicine, enabling treatments that are tailored to the individual patient’s genetic makeup.
Stem cell therapy is showing promise in the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases such as Parkinson’s and Alzheimer’s. By replacing damaged neurons with healthy ones derived from stem cells, researchers aim to restore lost functions and improve patients’ quality of life. Early clinical trials have demonstrated encouraging results, bringing us closer to effective therapies for these debilitating conditions.
In the realm of cardiovascular disease, stem cell therapy is also making significant headway. Scientists are exploring ways to regenerate heart tissue after a heart attack, potentially reducing the need for heart transplants. By injecting cardiomyocytes derived from stem cells into the damaged heart tissue, researchers hope to stimulate repair and improve heart function.
Orthopedic applications of stem cell therapy are another exciting area of progress. Conditions such as osteoarthritis and spinal cord injuries are being targeted with regenerative treatments that aim to restore joint function and promote healing of damaged cartilage and spinal tissue. These therapies offer a potential alternative to invasive surgeries and long-term reliance on pain medications.
Furthermore, stem cell therapy holds promise for the treatment of diabetes. By generating insulin-producing beta cells from stem cells, scientists are working towards a potential cure for type 1 diabetes. This approach could eliminate the need for daily insulin injections and significantly improve the quality of life for diabetic patients.
The field of oncology is also benefiting from advances in regenerative medicine. Stem cell transplants are being used to restore healthy bone marrow in cancer patients who have undergone intensive chemotherapy or radiation therapy. This treatment not only helps in recovering the immune system but also reduces the risk of relapse by ensuring the production of healthy blood cells.
Despite the remarkable progress, there are still challenges to overcome in the widespread implementation of stem cell therapy. Ethical considerations, potential immune rejection, and the need for rigorous clinical trials are some of the hurdles that researchers continue to address. However, ongoing advancements and increasing understanding of stem cell biology are paving the way for more effective and safe therapies.
In conclusion, regenerative medicine is advancing rapidly with the help of stem cell therapy, offering transformative potential for a wide range of diseases and injuries. As research progresses and new therapies are developed, the future of medicine looks increasingly promising, with the potential to significantly improve patient outcomes and revolutionize the treatment landscape.
We offer our respects and wish you a good reading. – Who Learns What? Team
- On-Site Comments