By becoming a member of our site, you can add the content you like to your favorites, and present the content you have produced or liked on the internet to our site visitors with the send content option.
Zaten bir üyeliğiniz mevcut mu ? Giriş yapın
By becoming a member of our site, you can add the content you like to your favorites, and present the content you have produced or liked on the internet to our site visitors with the send content option.
You Can Benefit from All Options Exclusive to Our Members by Registering

Next Content:
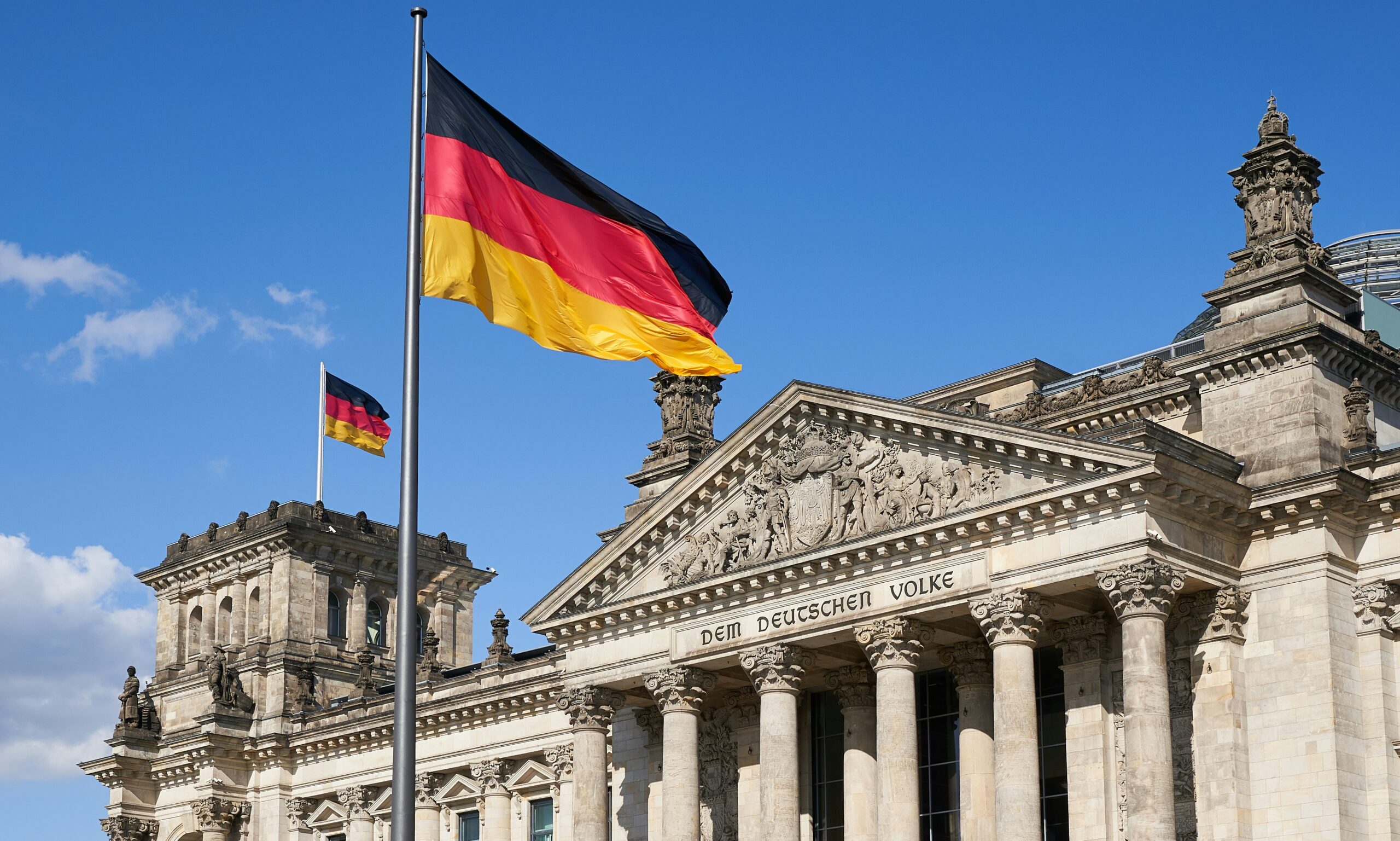
DAX 30 Growth Stocks: Germany’s Market Potential
Revolutionizing Diagnostics with Biosensors

In the realm of healthcare, biosensors are emerging as powerful tools for revolutionizing diagnostics, offering unprecedented capabilities in the detection and monitoring of diseases. These innovative devices combine biological sensing elements with transducers to convert biological responses into measurable signals, providing rapid, accurate, and cost-effective diagnostic solutions. Here’s how biosensors are transforming the landscape of diagnostics:
Enhanced Sensitivity and Specificity: Biosensors leverage biological recognition elements such as enzymes, antibodies, or nucleic acids to selectively bind to target molecules, enabling highly sensitive and specific detection. By harnessing the unique interactions between biological molecules, biosensors can detect even trace amounts of biomarkers associated with various diseases, including cancer, infectious diseases, and metabolic disorders.
Real-Time Monitoring: One of the key advantages of biosensors is their ability to provide real-time monitoring of biological parameters. Continuous monitoring of biomarkers in bodily fluids such as blood, saliva, or urine allows for early detection of diseases and timely intervention. This real-time feedback enables healthcare professionals to make informed decisions regarding patient care, leading to improved treatment outcomes and better disease management.
Point-of-Care Testing: Biosensors are well-suited for point-of-care testing, bringing diagnostic capabilities directly to the patient’s bedside or even into their homes. Miniaturized and portable biosensor devices enable rapid and decentralized testing, eliminating the need for centralized laboratory facilities and reducing turnaround times for test results. This accessibility is particularly valuable in remote or resource-limited settings where access to traditional diagnostic infrastructure may be limited.
Multiplexed Detection: Modern biosensors can simultaneously detect multiple analytes within a single sample, a capability known as multiplexed detection. By incorporating arrays of sensing elements or utilizing multiplexed detection techniques, biosensors can profile multiple biomarkers associated with a particular disease or physiological condition in a single assay. This multiplexing capability enhances diagnostic accuracy and provides a more comprehensive understanding of disease states.
Wireless Connectivity and Data Integration: Many biosensors are equipped with wireless connectivity capabilities, allowing for seamless data transmission to electronic devices such as smartphones or tablets. This connectivity enables remote monitoring of patient health status and facilitates data integration with electronic health records (EHRs) or cloud-based healthcare platforms. By leveraging wireless technology, biosensors enable remote patient monitoring and personalized healthcare delivery.
Customizable and Scalable Platforms: Biosensors offer a high degree of customization and scalability, allowing for the development of tailored diagnostic solutions to address specific clinical needs. Researchers and developers can design biosensors with different biological recognition elements, transduction mechanisms, and form factors to target diverse applications. This flexibility makes biosensors adaptable to a wide range of diagnostic challenges and enables rapid prototyping and commercialization of new diagnostic technologies.
Emerging Applications in Wearable Health Tech: Biosensors are increasingly being integrated into wearable health technologies, such as smartwatches, fitness trackers, and wearable patches. These wearable biosensors can continuously monitor physiological parameters such as heart rate, blood pressure, glucose levels, and sweat biomarkers in real time, providing valuable insights into individual health and wellness. By seamlessly integrating into everyday life, wearable biosensors empower individuals to take proactive control of their health and well-being.
Advancements in Nanotechnology and Materials Science: Ongoing advancements in nanotechnology and materials science are driving innovation in biosensor design and performance. Nanomaterials such as carbon nanotubes, graphene, and quantum dots offer unique properties that enhance the sensitivity, stability, and selectivity of biosensors. By leveraging nanomaterials and novel fabrication techniques, researchers are pushing the boundaries of biosensor capabilities and unlocking new possibilities for diagnostics and healthcare.
Regulatory Considerations and Commercialization Challenges: Despite their immense potential, biosensors face regulatory and commercialization challenges that must be addressed for widespread adoption in clinical practice. Regulatory agencies such as the FDA and EMA require rigorous validation and approval processes to ensure the safety, efficacy, and quality of biosensor-based diagnostic tests. Additionally, commercialization hurdles related to manufacturing scalability, cost-effectiveness, and reimbursement policies need to be overcome to realize the full clinical impact of biosensors.
In conclusion, biosensors are poised to revolutionize diagnostics by offering enhanced sensitivity, real-time monitoring, point-of-care testing, multiplexed detection, and seamless integration with wearable health technologies. As researchers continue to advance the field through innovations in nanotechnology, materials science, and wireless connectivity, biosensors will play an increasingly vital role in personalized medicine, disease management, and public health. By addressing regulatory and commercialization challenges, the full potential of biosensors can be realized, ushering in a new era of precision diagnostics and healthcare delivery.
We offer our respects and wish you a good reading. – Who Learns What? Team
- On-Site Comments