By becoming a member of our site, you can add the content you like to your favorites, and present the content you have produced or liked on the internet to our site visitors with the send content option.
Zaten bir üyeliğiniz mevcut mu ? Giriş yapın
By becoming a member of our site, you can add the content you like to your favorites, and present the content you have produced or liked on the internet to our site visitors with the send content option.
You Can Benefit from All Options Exclusive to Our Members by Registering

Next Content:
Blockchain in Healthcare Records Management
Renewable Energy Storage Innovations
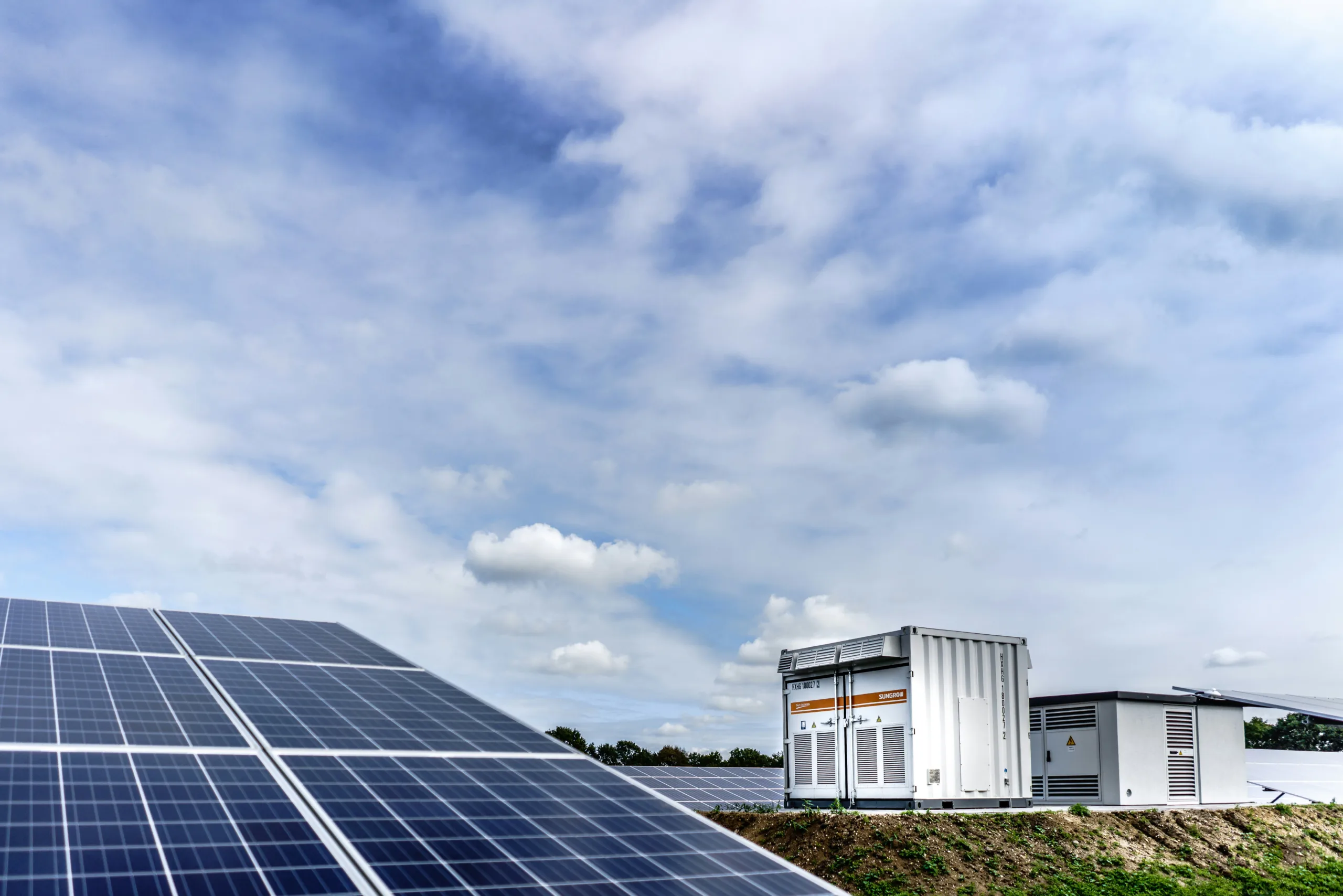

In the transition towards a sustainable energy future, the development of renewable energy storage solutions plays a pivotal role in overcoming one of the biggest challenges of renewable energy integration: intermittency. As renewable energy sources such as solar and wind become increasingly prominent, there is a growing need for innovative storage technologies to store excess energy generated during periods of high production and release it when demand is high or generation is low.
One of the most promising innovations in renewable energy storage is the advancement of battery technology. Lithium-ion batteries, in particular, have emerged as a frontrunner due to their high energy density, fast charging capabilities, and declining costs. These batteries are not only used in electric vehicles but also in stationary energy storage systems, such as grid-scale battery storage facilities and residential energy storage units.
Another area of innovation lies in pumped hydro storage. This traditional form of energy storage involves pumping water uphill during times of low demand and releasing it through turbines to generate electricity during peak demand periods. While pumped hydro storage has been utilized for decades, recent innovations in modular and closed-loop systems have made it more flexible and cost-effective, especially in regions with suitable geography.
Furthermore, thermal energy storage technologies are gaining traction as efficient and scalable solutions for storing excess heat generated from renewable sources such as solar thermal power plants. These systems use materials with high heat capacity to store thermal energy during the day and release it on demand, providing a reliable source of dispatchable power even when the sun is not shining.
Additionally, hydrogen is emerging as a versatile energy carrier and storage medium for renewable energy. Through processes such as electrolysis, renewable electricity can be used to split water molecules into hydrogen and oxygen. The hydrogen can then be stored and transported for later use in fuel cells to generate electricity or as a feedstock for industrial processes.
In conclusion, the ongoing innovations in renewable energy storage are driving significant advancements in the reliability, affordability, and scalability of renewable energy systems. By overcoming the challenges of intermittency and grid integration, these storage technologies are accelerating the transition towards a more sustainable and resilient energy future.
We offer our respects and wish you a good reading. – Who Learns What? Team!
Dont forget the comment here mate! 🙂 you can connect us!
- On-Site Comments