By becoming a member of our site, you can add the content you like to your favorites, and present the content you have produced or liked on the internet to our site visitors with the send content option.
Zaten bir üyeliğiniz mevcut mu ? Giriş yapın
By becoming a member of our site, you can add the content you like to your favorites, and present the content you have produced or liked on the internet to our site visitors with the send content option.
You Can Benefit from All Options Exclusive to Our Members by Registering

Next Content:
Renewable Fashion: A Sustainable Revolution in Clothing and Textiles
- Home Page
- #Advancements
- Nanotechnology Applications: Exploring Advancements and Potential Risks
Nanotechnology Applications: Exploring Advancements and Potential Risks
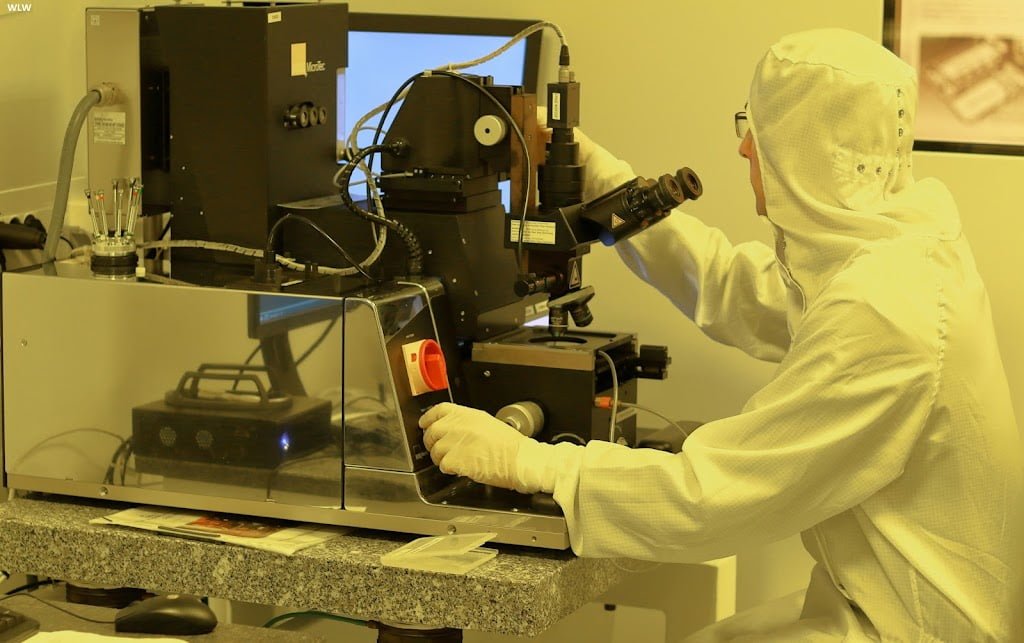

Nanotechnology, the manipulation of matter at the nanoscale, has emerged as a revolutionary field with a wide range of applications across various industries. From medicine and electronics to energy and environmental science, nanotechnology offers promising solutions to some of the most pressing challenges facing society. However, along with its potential benefits come concerns about potential risks and ethical implications. In this article, we explore the advancements and potential risks associated with nanotechnology applications.
Advancements in Nanotechnology Applications
Nanotechnology has unlocked a plethora of possibilities for innovation and advancement across diverse fields:
-
Medicine: In healthcare, nanotechnology holds the promise of revolutionizing diagnosis, treatment, and drug delivery. Nanoscale particles can be engineered to target specific cells or tissues, enabling more precise and effective therapies for diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and neurodegenerative disorders.
-
Electronics: The electronics industry has benefited greatly from nanotechnology, with the development of smaller, faster, and more efficient devices. Nanoscale materials and structures enable the fabrication of high-performance transistors, sensors, and displays, leading to advancements in computing, telecommunications, and consumer electronics.
-
Energy: Nanotechnology offers solutions for sustainable energy production and storage. Nanomaterials such as quantum dots and nanowires are being explored for use in solar cells, batteries, and fuel cells, promising to enhance energy efficiency and reduce reliance on fossil fuels.
-
Environmental Remediation: Nanotechnology has the potential to address environmental challenges such as pollution and water scarcity. Nanoparticles can be used to remove contaminants from soil and water, filter pollutants from air, and facilitate the cleanup of hazardous waste sites.
-
Materials Science: Nanotechnology has revolutionized the field of materials science, enabling the development of stronger, lighter, and more durable materials. Nanocomposites and nanocoatings offer enhanced mechanical, thermal, and electrical properties, leading to applications in aerospace, automotive, and construction industries.
Risks and Ethical Considerations
Despite its potential benefits, nanotechnology also raises concerns about potential risks to human health, safety, and the environment:
-
Health Risks: The small size and unique properties of nanoparticles raise concerns about their potential toxicity and long-term effects on human health. Studies have shown that certain nanoparticles may have adverse effects on cells, tissues, and organs, leading to inflammation, oxidative stress, and other health problems.
-
Environmental Impacts: Nanomaterials released into the environment through manufacturing processes, product use, and waste disposal may accumulate in ecosystems and impact biodiversity. There is also concern about the potential for nanomaterials to bioaccumulate in living organisms and disrupt ecological processes.
-
Ethical Implications: The rapid pace of nanotechnology development raises ethical questions about its societal implications, including issues of equity, access, and control. There is debate about who benefits from nanotechnology advancements and who bears the risks, as well as concerns about potential misuse or unintended consequences.
We offer our respects and wish you a good reading. – Who Learns What? Team!
- On-Site Comments