By becoming a member of our site, you can add the content you like to your favorites, and present the content you have produced or liked on the internet to our site visitors with the send content option.
Zaten bir üyeliğiniz mevcut mu ? Giriş yapın
By becoming a member of our site, you can add the content you like to your favorites, and present the content you have produced or liked on the internet to our site visitors with the send content option.
You Can Benefit from All Options Exclusive to Our Members by Registering

Next Content:
Virtual Beings: Exploring the Emergence of AI-Powered Personalities
- Home Page
- #bioengineering
- Biofabrication: Growing Sustainable Materials in the Lab
Biofabrication: Growing Sustainable Materials in the Lab
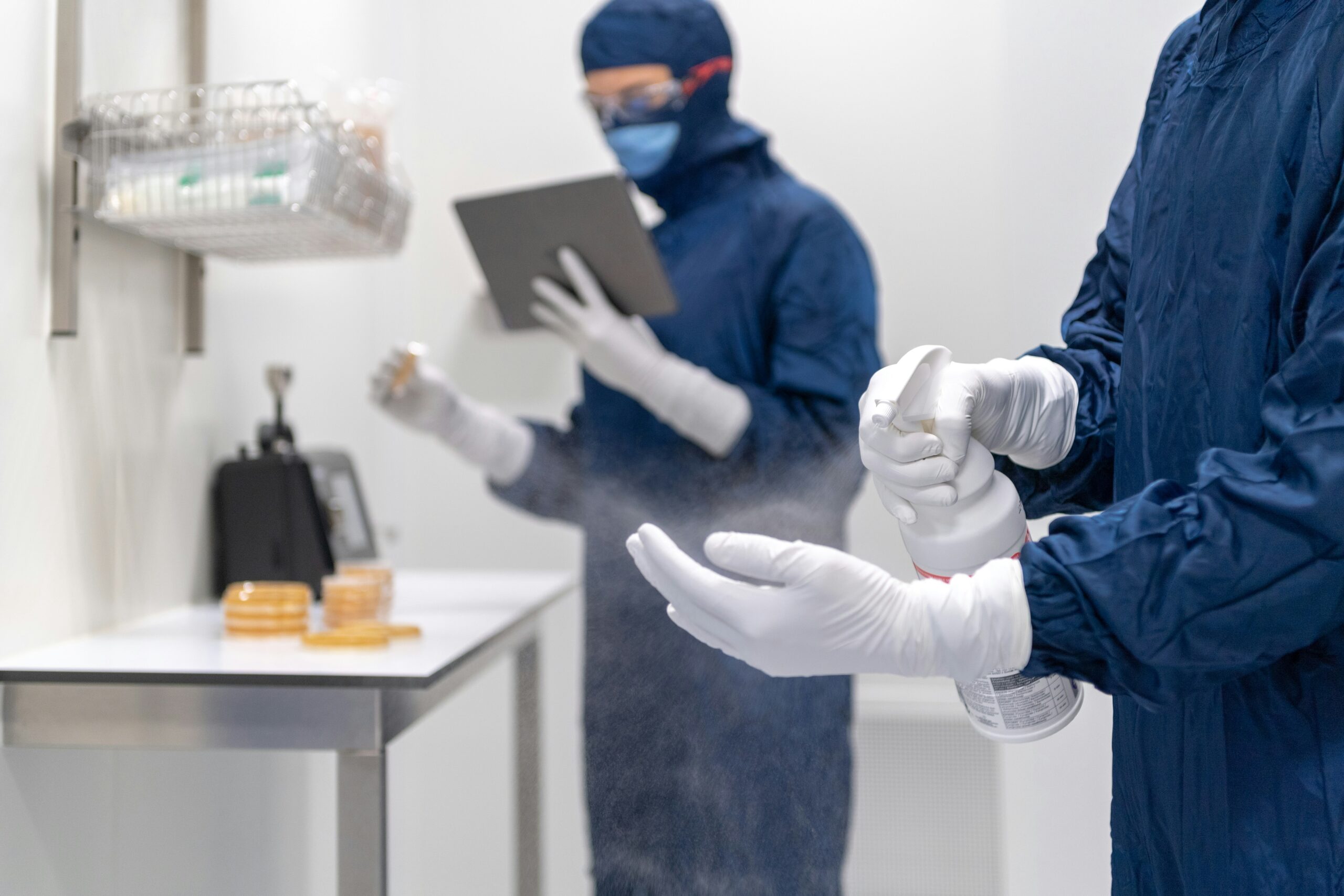

Biofabrication is revolutionizing the production of sustainable materials by enabling scientists to grow these materials directly in the lab. This innovative approach merges biology with engineering, offering eco-friendly alternatives to traditional manufacturing processes and addressing pressing environmental concerns.
One of the primary benefits of biofabrication is its potential to reduce environmental impact. Traditional manufacturing often relies on resource-intensive processes and generates significant waste and emissions. In contrast, biofabrication uses biological systems, such as bacteria, fungi, and plant cells, to produce materials with minimal waste and energy consumption. This makes it a highly sustainable and eco-friendly method of production.
A notable example of biofabrication is the development of mycelium-based materials. Mycelium, the root structure of fungi, can be cultivated to create a variety of products, from packaging materials to building insulation. These biodegradable alternatives can replace plastics and other non-renewable resources, significantly reducing pollution and waste.
Another exciting advancement in biofabrication is the creation of lab-grown leather. By using animal cells to grow leather in controlled environments, companies can produce high-quality leather without the environmental and ethical issues associated with traditional livestock farming. This sustainable leather offers the same durability and aesthetic appeal as conventional leather but with a much smaller ecological footprint.
Biofabrication also holds promise for the textile industry. Researchers are developing biofabricated fabrics using yeast and bacteria to produce cellulose-based fibers. These fibers can be used to create textiles that are not only sustainable but also possess unique properties such as enhanced strength and biodegradability. This innovation has the potential to transform the fashion industry by reducing its reliance on synthetic fibers and minimizing its environmental impact.
In addition to textiles and packaging, biofabrication is making strides in the field of construction. Scientists are exploring the use of bio-concrete, which incorporates bacteria to induce the formation of calcium carbonate. This process not only strengthens the concrete but also repairs cracks, extending the lifespan of buildings and infrastructure. Such advancements in sustainable construction materials can lead to more durable and environmentally friendly building practices.
Furthermore, biofabrication is contributing to the development of medical materials. Researchers are creating bioengineered tissues and organs for transplantation, addressing the shortage of donor organs and reducing the risk of rejection. These lab-grown tissues can also be used for drug testing and disease modeling, accelerating the development of new treatments and therapies.
Despite the remarkable progress, biofabrication faces challenges that need to be addressed for widespread adoption. Scalability, cost efficiency, and regulatory approval are some of the hurdles that researchers and companies must overcome. However, with continuous advancements in biotechnology and material science, these challenges are becoming increasingly surmountable.
In conclusion, biofabrication represents a groundbreaking approach to producing sustainable materials in the lab. By harnessing the power of biological systems, this innovative field offers eco-friendly alternatives to traditional manufacturing processes, with applications ranging from packaging and textiles to construction and medicine. As research progresses and technology advances, biofabrication has the potential to play a pivotal role in creating a more sustainable and environmentally conscious future.
We offer our respects and wish you a good reading. – Who Learns What? Team
- On-Site Comments